A person with physical disabilities can’t interact with the world the same way as the able, but there’s no reason we can’t use tech to close that gap. Loro is a device that mounts to a wheelchair and offers its occupant the ability to see and interact with the people and things around them in powerful ways.
Loro’s camera and app work together to let the user see farther, read or translate writing, identify people, gesture with a laser pointer and more. They demonstrated their tech onstage today during Startup Battlefield at TechCrunch Disrupt Berlin.
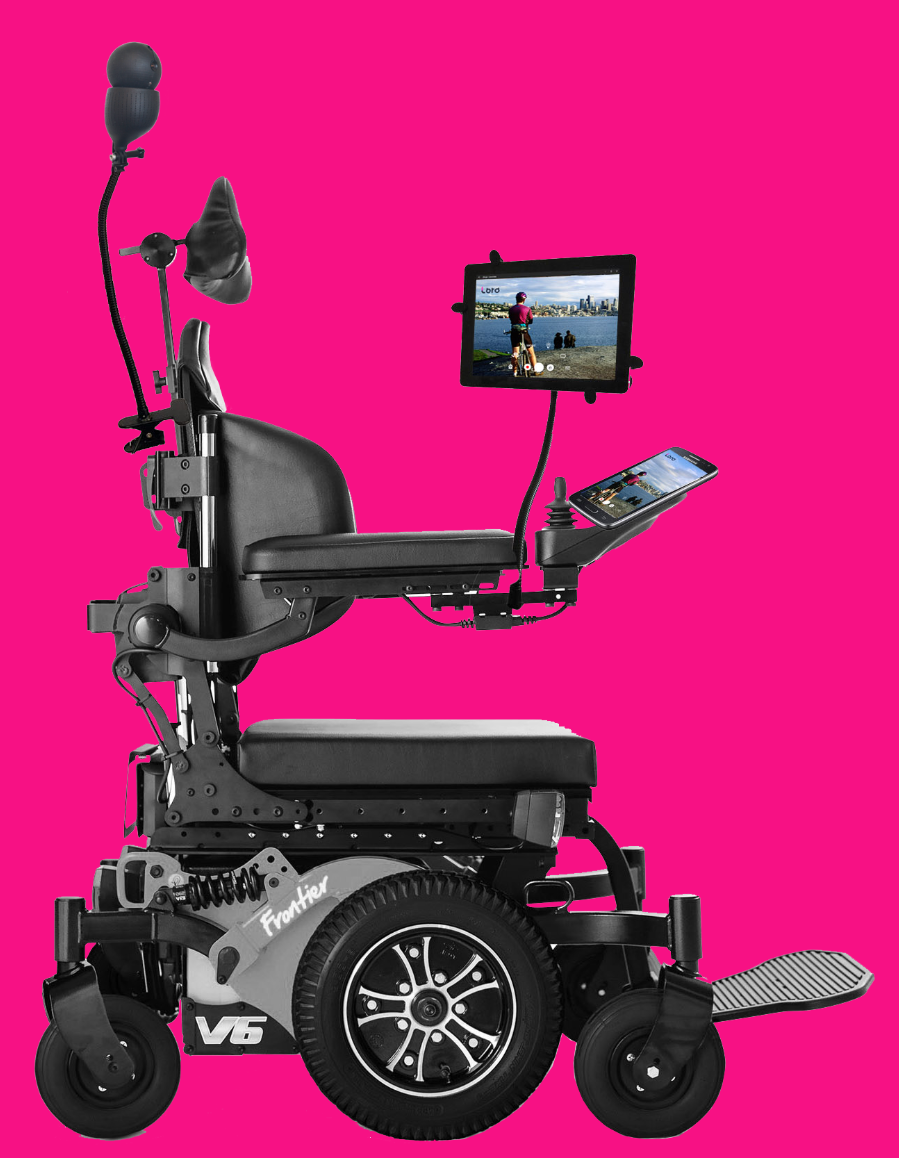 Invented by a team of mostly students who gathered at Harvard’s Innovation Lab, Loro began as a simple camera for disabled people to more easily view their surroundings.
Invented by a team of mostly students who gathered at Harvard’s Innovation Lab, Loro began as a simple camera for disabled people to more easily view their surroundings.
“We started this project for our friend Steve,” said Loro co-founder and creative director, Johae Song. A designer like her and others in their friend group, he was diagnosed with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, or ALS, a degenerative neural disease that paralyzes the muscles of the afflicted. “So we decided to come up with ideas of how to help people with mobility challenges.”
“We started with just the idea of a camera attached to the wheelchair, to give people a panoramic view so they can navigate easily,” explained co-founder David Hojah. “We developed from that idea after talking with mentors and experts; we did a lot of iterations, and came up with the idea to be smarter, and now it’s this platform that can do all these things.”
It’s not simple to design responsibly for a population like ALS sufferers and others with motor problems. The problems they may have in everyday life aren’t necessarily what one would think, nor are the solutions always obvious. So the Loro team determined to consult many sources and expend a great deal of time in simple observation.
“Very basic observation — just sit and watch,” Hojah said. “From that you can get ideas of what people need without even asking them specific questions.”
Others would voice specific concerns without suggesting solutions, such as a flashlight the user can direct through the camera interface.
“People didn’t say, ‘I want a flashlight,’ they said ‘I can’t get around in the dark.’ So we brainstormed and came up with the flashlight,” he said. An obvious solution in some ways, but only through observation and understanding can it be implemented well.
The focus is always on communication and independence, Song said, and users are the ones who determine what gets included.
“We brainstorm together and then go out and user test. We realize some features work, others don’t. We try to just let them play with it and see what features people use the most.”
There are assistive devices for motor-impaired people out there already, Song and Hojah acknowledged, but they’re generally expensive, unwieldy and poorly designed. Hojah’s background is in medical device design, so he knows of what he speaks.
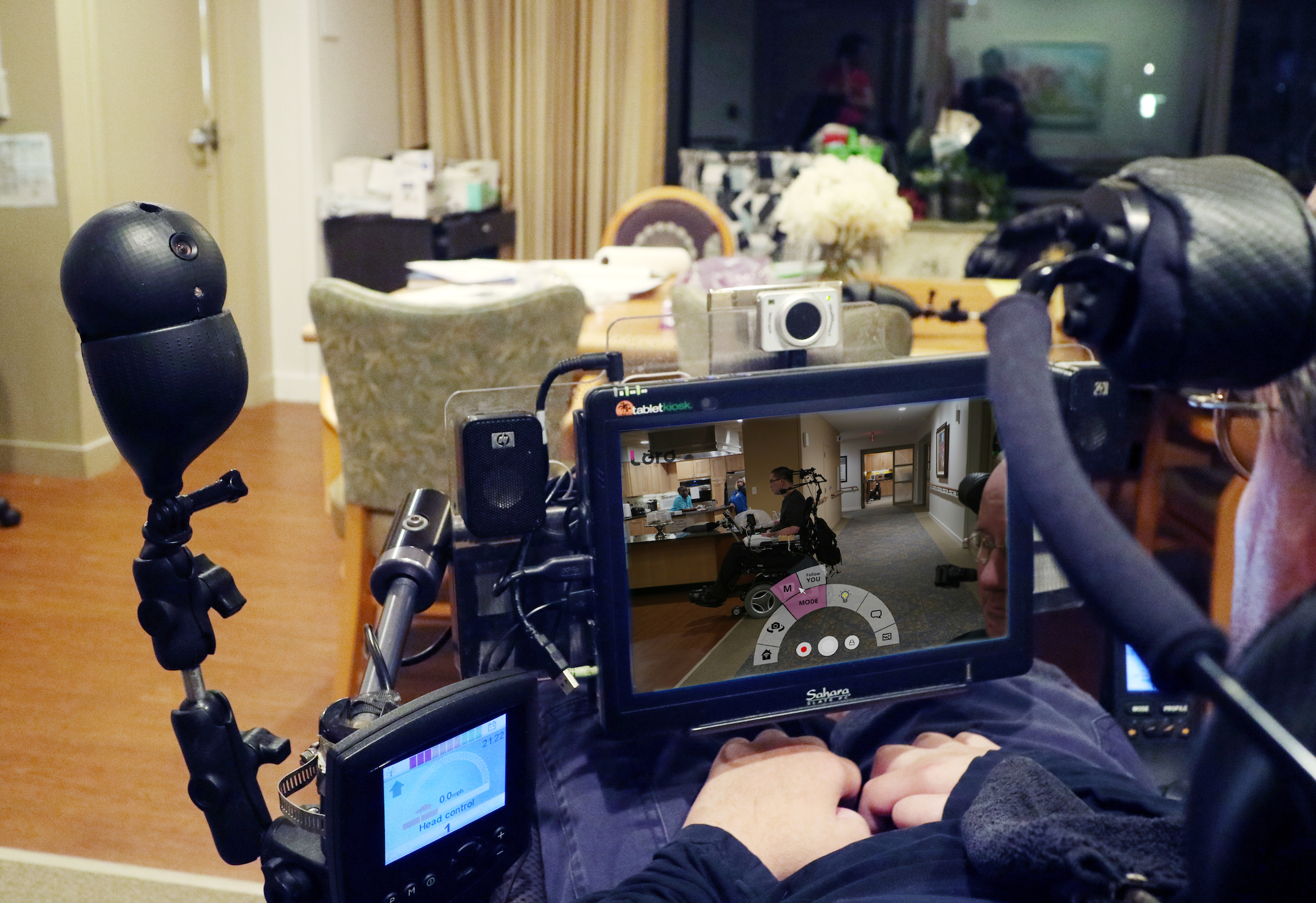
Consequently, Loro has been designed to be as accessible as possible, with a tablet interface that can be navigated using gaze tracking (via a Tobii camera setup) or other inputs like joysticks and sip-and-puff tubes.
The camera can be directed to, for example, look behind the wheelchair so the user can safely back up. Or it can zoom in on a menu that’s difficult to see from the user’s perspective and read the items off. The laser pointer allows a user with no ability to point or gesture to signal in ways we take for granted, such as choosing a pastry from a case. Text to speech is built right in, so users don’t have to use a separate app to speak out loud.
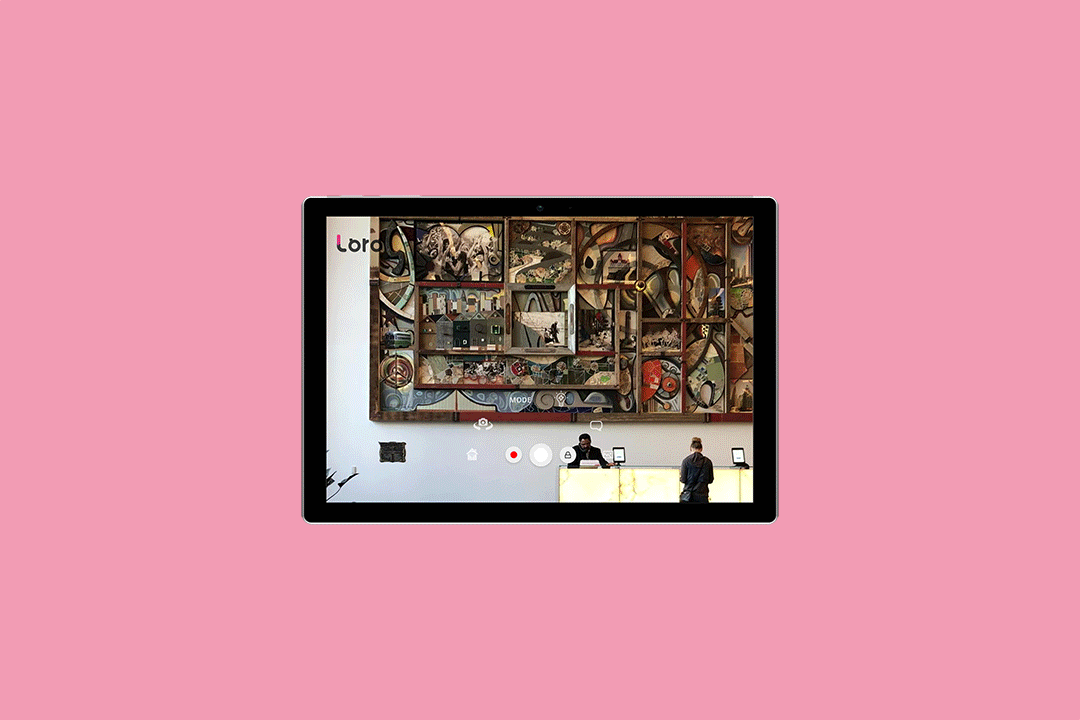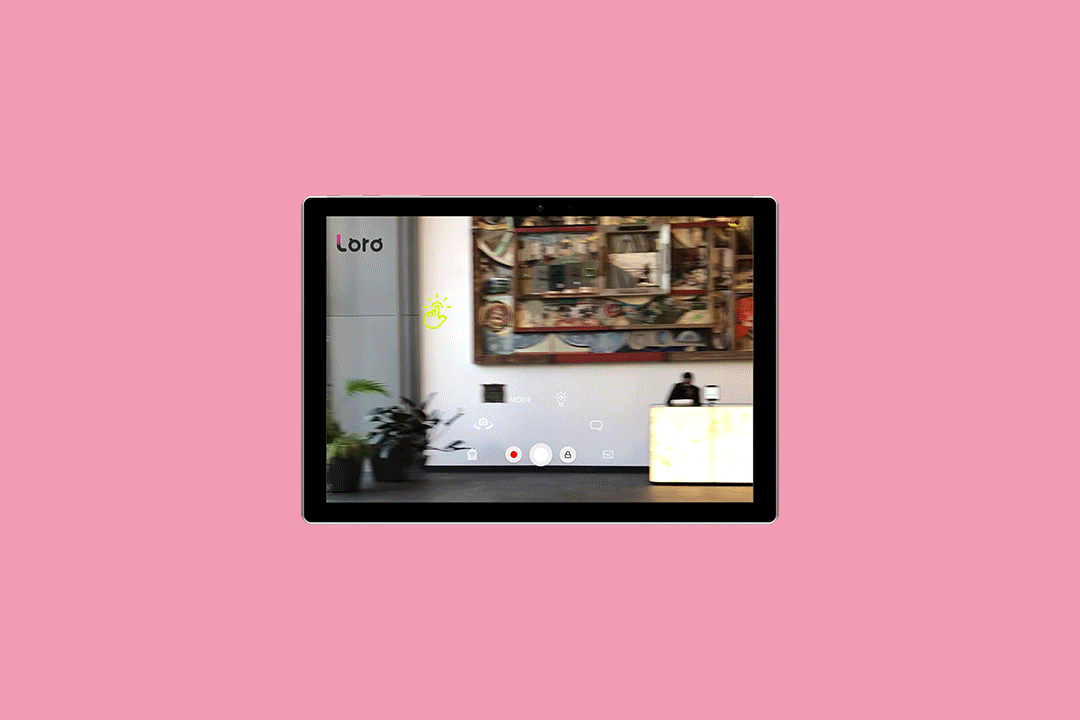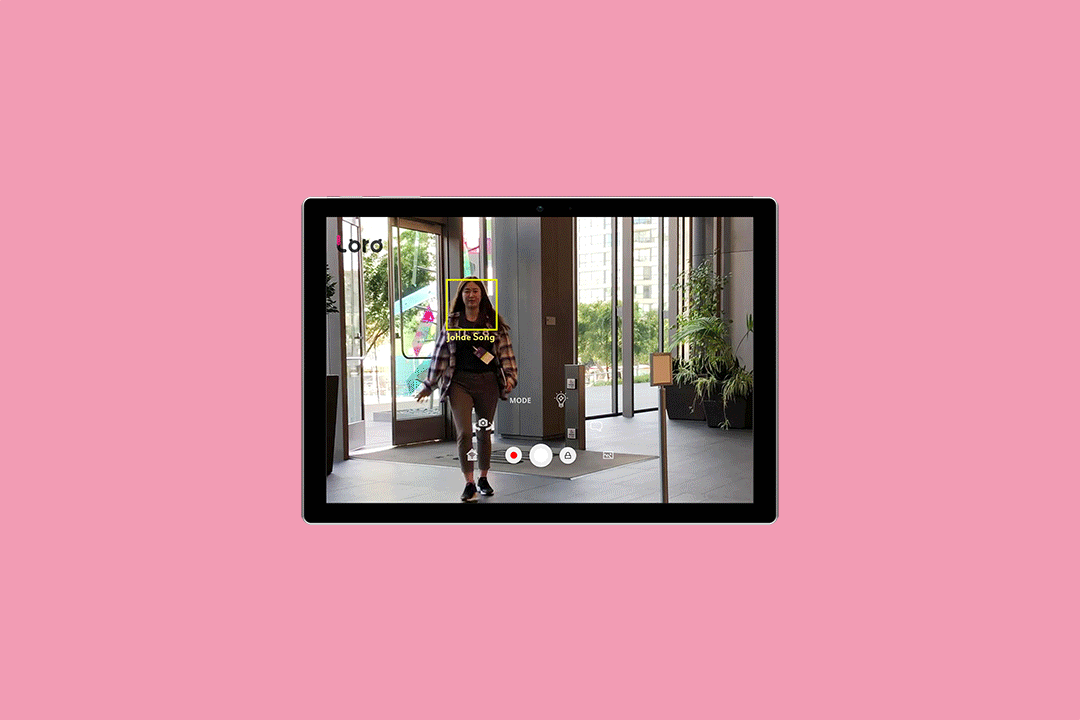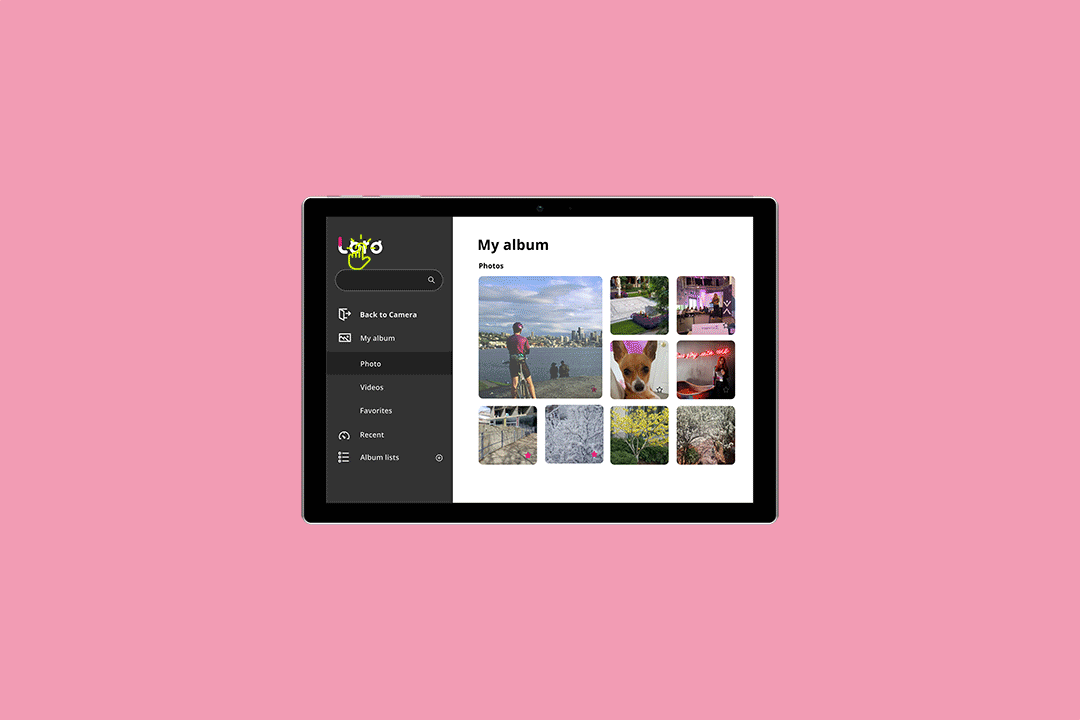
The camera also tracks faces and can recognize them from a personal (though for now, cloud-hosted) database for people who need help tracking those with whom they interact. The best of us can lose a name or fail to place a face — honestly, I wouldn’t mind having a Loro on my shoulder during some of our events.
Right now the team is focused on finalizing the hardware; the app and capabilities are mostly finalized but the enclosure and so on need to be made production-ready. The company itself is very early-stage — they just incorporated a few months ago and worked with $100,000 in pre-seed funding to create the prototype. Next up is doing a seed round to get ready to manufacture.
“The whole team, we’re really passionate about empowering these people to be really independent, not just waiting for help from others,” Hojah said. Their driving force, he made clear, is compassion.
[gallery ids="1752219,1752224,1752228,1752229,1752230"]
from Gadgets – TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2zvpnlU


Comments
Post a Comment